How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from understanding your drone’s components to mastering advanced flight techniques. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, essential controls, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-prepared for a successful and enjoyable flight experience.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to operate a drone responsibly and proficiently. We will delve into the intricacies of drone mechanics, safety protocols, and advanced flight maneuvers, providing a thorough understanding of this increasingly popular technology.
Drone Parts and Components: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s functionality, from propulsion and stability to navigation and image capture.
Drone Component Functions
The major components of a drone work in concert to achieve flight. A brief overview of their individual roles is provided below.
| Component | Function | Type | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and propulsion. | Typically plastic or carbon fiber; various sizes and designs. | Regular inspection for damage; replace if bent or cracked. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers; convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. | Brushless DC motors (BLDC) are common; brushed motors are less efficient and durable. | Check for loose screws or unusual sounds; consider professional servicing if necessary. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes sensor data and controls motor speed to maintain stability and execute commands. | Microcontroller-based unit with various sensor inputs (IMU, barometer, GPS). | Generally requires minimal maintenance; firmware updates may be necessary. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are prevalent; different voltage and capacity ratings. | Proper charging and storage are crucial; avoid overcharging or deep discharging. |
| GPS | Provides location data for navigation and positioning. | GPS receiver module; communicates with GPS satellites. | Ensure clear view of the sky for optimal signal reception. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Various resolutions and features; often integrated with gimbal for stabilization. | Lens cleaning; protect from impacts. |
Drone Battery Types and Characteristics
Drone batteries are typically Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries. They are known for their high energy density, but require careful handling and maintenance. Different types offer varying flight times and performance characteristics.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively handle your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This guide will help you understand the basics of piloting and navigating your drone, ensuring a successful and safe flight experience every time.
Proper drone operation requires practice and understanding of relevant regulations.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): High energy density, lightweight, but require careful charging and storage to prevent damage or fire. Common voltages include 3S (11.1V), 4S (14.8V), and 6S (22.2V), with higher voltages generally providing longer flight times.
- LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage): Similar to LiPo but with a higher voltage per cell, offering slightly increased flight time and power.
Brushless vs. Brushed Motors
Brushless motors are far more common in modern drones due to their higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and greater power output compared to brushed motors. Brushed motors are simpler but generate more heat and wear out quicker.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for safe drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow this comprehensive checklist:
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check battery level and ensure it is properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal acquisition (sufficient number of satellites).
- Check the surrounding area for obstacles and hazards.
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Confirm that all communication systems (controller, drone) are functioning correctly.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration (if necessary).
Safe Drone Operation Best Practices
Safe drone operation requires adherence to regulations and best practices. Understanding airspace restrictions and emergency procedures is crucial.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Avoid flying over crowds or people.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures, such as battery failure or loss of control.
Understanding Local Drone Laws
Drone laws and regulations vary significantly by location. It is crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before operating your drone.
Safe Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual flowchart would illustrate the sequential steps in a safe pre-flight procedure. The flowchart would begin with “Power On Controller” and proceed through battery check, propeller inspection, GPS signal verification, and airspace check, culminating in a “Ready to Fly” confirmation. A separate branch would depict actions in case of any problems encountered during the checklist.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing
The processes of takeoff, flight, and landing should be performed smoothly and safely. Understanding throttle control and different flight modes is key.
Safe Takeoff Procedures
A safe takeoff involves gradually increasing throttle while monitoring the drone’s stability. It’s important to ensure the drone is level and stable before ascending.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal lock.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Maintain a stable hover before proceeding to further maneuvers.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and stability. GPS mode relies on GPS signals for position holding, while Attitude mode relies on the drone’s internal sensors.
- GPS Mode: Maintains position and altitude using GPS data; ideal for stable shots and filming.
- Attitude Mode: Relies on internal sensors for orientation; useful for more agile maneuvers but requires more pilot skill.
Smooth and Controlled Landing
Landing should be performed gradually and smoothly, avoiding sudden drops. A gentle descent is crucial for protecting the drone and its components.
- Slowly lower the throttle to descend.
- Maintain a slow and controlled descent.
- Gently place the drone on a stable surface.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Step-by-Step Drone Flight Guide
A step-by-step guide with accompanying images would visually demonstrate a successful drone flight. Image 1: Pre-flight checks; Image 2: Safe takeoff; Image 3: Hovering; Image 4: Maneuvering; Image 5: Controlled landing; Image 6: Post-flight inspection.
Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvering
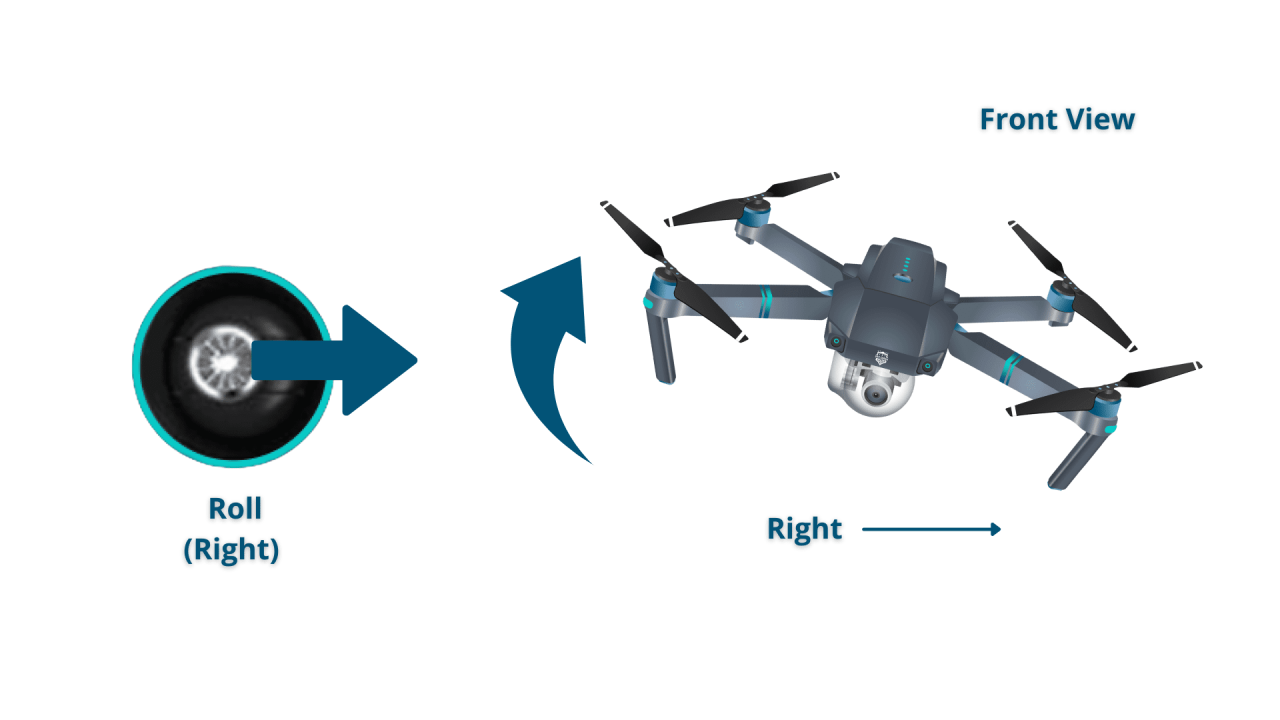
Understanding drone flight controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Each control stick influences a specific aspect of the drone’s movement.
Drone Control Stick Functions
The control sticks typically control pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle.
| Control Stick | Effect on Drone |
|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical): Throttle | Controls ascent and descent. |
| Left Stick (Horizontal): Roll | Controls tilting left and right. |
| Right Stick (Vertical): Pitch | Controls tilting forward and backward. |
| Right Stick (Horizontal): Yaw | Controls rotation around the vertical axis. |
Common Drone Maneuvers
Common maneuvers include hovering, turning, ascending, and descending. Mastering these maneuvers is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
Stable Flight in Windy Conditions, How to operate a drone
Flying in windy conditions requires careful control and anticipation. Maintaining stable flight in wind requires skillful adjustments to compensate for wind gusts.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography
Drone cameras offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and techniques is key to achieving high-quality results.
Drone Camera Settings
Typical drone camera settings include shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. These settings influence the exposure and overall image quality.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s shutter remains open, affecting motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field and light intake.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light, affecting image noise.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media

Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires careful planning and execution. Consider lighting, composition, and camera angles for optimal results.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles and perspectives can dramatically change the mood and impact of your aerial shots. Experiment with various angles to find the best perspective for your subject.
Transferring Images and Videos
Transferring images and videos from the drone to a computer can be accomplished through various methods, such as using a memory card reader or wirelessly transferring files via Wi-Fi or mobile application.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drones can experience malfunctions. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting steps is crucial for minimizing downtime.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Common drone malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor failure. Quick identification and resolution are key.
Troubleshooting Steps
A troubleshooting guide with bullet points would detail the steps to diagnose and resolve typical problems. For example, low battery would involve checking the battery level and charging it; GPS signal loss would involve checking for obstructions and ensuring a clear view of the sky; motor failure would involve checking for loose connections or physical damage.
Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular drone maintenance and cleaning are essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning propellers, checking for loose parts, and inspecting the battery for damage.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced drone techniques allow for more complex and autonomous flights. These techniques often involve specialized software and hardware.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques such as waypoint navigation and automated flight allow for pre-planned and complex flight paths. These features are particularly useful for aerial photography and surveying.
Drone Software for Flight Planning
Drone software enables users to plan and execute complex flights by setting waypoints, adjusting altitude, and defining flight parameters. This simplifies the process of capturing specific aerial shots or conducting surveys.
Drone Flight Controllers
Different drone flight controllers offer varying capabilities and features. Some controllers may support advanced features like obstacle avoidance or autonomous flight, while others may be more basic.
Sample Flight Plan Using Waypoints

A sample flight plan using waypoints would Artikel a specific flight path. The plan would include a starting point, a series of waypoints defining the desired route, and an ending point. The expected flight path would be a smooth transition between each waypoint, maintaining the specified altitude and speed.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. By carefully following the pre-flight checklist, understanding the flight controls, and practicing safe flying techniques, you’ll be well on your way to capturing stunning aerial footage and exploring the limitless potential of drone technology. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations.
Happy flying!
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and autonomous features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to check out is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. If GPS is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, maintaining visual contact and having a backup plan is crucial.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations in your area.
